This product is not exportable outside the United States.
By adding this item to cart, you agree and acknowledge the Export Policy and confirm that you are a person in the United States with no intentions to illegally export the device.
This product is not exportable outside the United States.
By adding this item to cart, you agree and acknowledge the Export Policy and confirm that you are a person in the United States with no intentions to illegally export the device.


0

0


Humanity isn't sitting still at all. We want to go faster, to fly higher, to know more about the world and to see further! The last aspiration for four hundred years is a variety of optical devices. There are telescopes, spyglasses, and perhaps the most charismatic and popular of the optics are binoculars and scopes.
When choosing a new sight or binoculars, it is easy for a person to get confused and not understand the whole technical component of an optical device. If you want to understand better and compare your choice with analogs - not only by size, weight and price, it is better to study the device characteristics.
Just for this case, here are a few important terms explained in common terms.
The most important indicators for optical sights and binoculars are:
About the diameter of the lenses and the twilight number, we understand from a high school physics course more or less. Then the field of vision often confuses the user.
In this article, we will try to tell you as much as possible about one of the most important parameters of optical devices. It is a field of view.
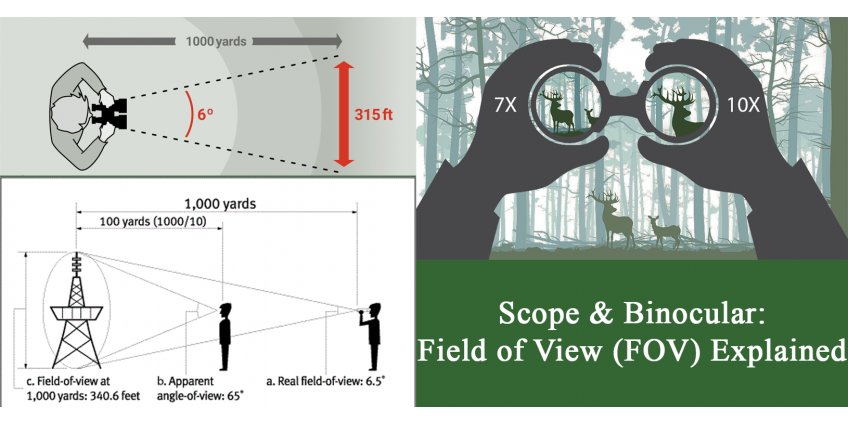
The field of view (FOV) is a maximum linear distance horizontally, which can be seen through the reticle at a distance of 100 m (for American sights the FOV value is often specified in feet at a distance of 100 yards). For example, the field of view of a variable magnification reticle at three-fold magnification (3x) is usually slightly more than 10.5 m at 100 m (30 ft 100 yards), and at nine-fold magnification (9x) it is about 4.7 m by 100 m (14 ft 100 yards). An increase in lens size does not affect this value in any way.
You read the previous paragraph and realized you didn't understand anything? Or did you partially understand it? Don't get upset! We'll make it easier for you now.
The field of view is the size of the imaginary image (round picture) that you see when you look through an optical device. Simply put, it is part of the space observed in the telescope sight or binoculars.
The field of view is influenced by the diameter of the optical system lens and the distance from the shooter’s eye to the eyepiece. In any case, the larger the magnification of the sight, the smaller the field of view. The magnified scope allows you to observe a wide field of view at low magnification and easily find the target, then rotate the ring on the tube to enlarge the image and make an accurate aiming.
There are so-called "wide-angle" sights, which have a larger field of view by 20-40° in comparison with conventional sights.
How is Field of View Measured? (H2)
In the case of magnified sights, it is most often indicated at a distance of 100 meters or 100 yards. For example, 42.5 meters by 100 meters or 127.5 inches by 100 yards may be indicated. As an alternative value, the field of view may be expressed in degrees. For example, 6.6.
- Whoa, whoa, whoa! - you say, you promised to speak in plain language!
And you're right. FOV of binoculars is measured in feet at a distance of 1,000 yards. The sights measure the FOV in feet per 100 yards. If the characteristics of the binoculars tell you that the field of view of the device is 340 feet by 1,000 yards, it means that you will see the picture of 340 feet (from left to right), at the distance of 1,000 yards from you.
And there are also devices with an angular field of view. The higher the angle, the wider the field of view.
To convert the angular field of view into a linear one you just need to multiply the specified angle by 52.5. Why? One angle equals 52.5 feet. It's simple!
The angle of view is closely related to the magnification of the reticle: the larger the magnification, the smaller the angle of view. This means that the larger the magnification, the smaller the angle of view. It is clear that a moving object will be harder to shoot with a telescope sight that has a smaller field of view. Therefore, when choosing the telescope sight on the field of view it is necessary to take into account the shooting distance and capabilities of the weapon, determining the most optimal ratio of magnification and angle of view.
Moreover, the greater the multiplicity, the smaller the field of view, and the harder it becomes to hold a binocular or sight still to maintain a stable image. When choosing a binocular or reticle for prolonged handheld observation, keep in mind that the multiplicity should not exceed 10x. Test several devices with different magnification to see the difference. Try to see small details in the image; often you may see more details in the scope with smaller magnification because of the more stable position of the image.
Another parameter is the relief of the eyes. Often, if the removal of the exit pupil is too small, it is possible to see its darkening at the edge of the field of vision. Technically, vignetting is the reduction in brightness or saturation of the image at its periphery compared to the center. To put it crudely, you have to look from the optimum distance. If the object is too close or too far away, the optics may lose part of the image along the edges, darkening it.
Well, we hope our article was useful for you. And maybe the previously unclear parameters of optics have now become clear to you.
More information here:
Laser Range Finding Rifle Scopes
Rifle Scope Glossary of Terms
How to Choose Best Scope Covers & Caps
In our store
Table of contents
Featured Articles
ENVG-B. Enhanced night vision goggles–binocular. Thermal vision monoculars. Night vision monoculars. Thermal vision binoculars. Night vision binocular..
Which thermal scopes are the best for hunting? We will answer this question. Our TOP 5 best thermal scopes. What are their functions, how do they work..
Different types of the Scope Mount their differences and methods of attachment to weapons are discussed in this article...
Monocular vs Binoculars – What’s Better? Review of binoculars and monoculars. Priority device for different activities. Comparison of binoculars and ..
Today we'll talk about covers and caps, and help you find the perfect one for your scope. Let's take a look at some of the most popular consumer choic..