
Become a part of our community!
Subscribe to our news and mailing lists and be aware of all the news and discounts. Our new promotions and opportunities will always be with you just a click away.
Join and live in the same rhythm with us!
Become a part of our community!

Subscribe to our news and mailing lists and be aware of all the news and discounts. Our new promotions and opportunities will always be with you just a click away.
Join and live in the same rhythm with us!
This product is not exportable outside the United States.
By adding this item to cart, you agree and acknowledge the Export Policy and confirm that you are a person in the United States with no intentions to illegally export the device.
 928-333-4300
928-333-4300


0

0


Night Vision has
become a popular discussion point and search in recent years, due to ability to
allow users to see at night. Polarized between the advantages shown through
Hollywood, and utilization used in the military, there is a mystique
surrounding Night Vision on what it’s capabilities are, advantage it offers,
and the variances between the different generations of quality. The main
difference between night vision and thermal imaging is that night vision
amplifies ambient light that may not be visible to the naked eye whereas thermal
imaging amplifies heat. For the purpose of this article, we are going to focus
on what night vision is, how it works and how night vision varies from thermal imaging.
Night Vision
amplifies ambient light that may not be visible to the naked eye, and allows
you to see in darkness. Night vision is broken down into multiple generations,
each offering a higher level of performance (ranging from Gen1 – Gen3, as well
as Digital Night Vision). Night Vision technology uses various types of image
intensifier tubes that convert weak light from the visible and near-infrared
spectrum to visible light detectable by a human eye. Allowing people to see in
semi dark or full darkness with the help of IR illumination or ambient light.Night
Vision amplifies this ambient light by passing through electron chargedintensifier
tubes. All night vision devices are very
sensitive to light, and are possible to damage by exposing to sunlight,
headlights from cars, or from too much direct light.
Night Vision
capabilities do range from the generation of the device, the quality of the
tube within the unit, as well as the overall capabilities of the device itself.
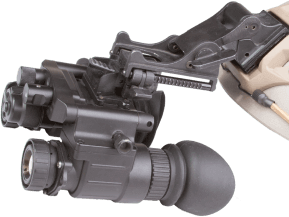
Night Vision comes in monoculars, goggles / helmet mounted, binoculars, and
weapons mounted. Typically, all goggles/helmet mounted units will be offered
only in a 1x magnification (same as your naked eye). Reason for this is that if
you are walking or driving a vehicle, your depth perception is not altered by
the added magnification. Monoculars, binoculars and weapons mountable all are
available in multiple magnifications;however, 5x or 7x are typically the
highest magnifications offered. This is attributed to each increase in
magnification, an additional magnified glass lens is stacked in front of the
tube assembly. Since night vision is relying on how much ambient light can be
collected at a given distance, each additional lens (magnification) means that
less light is able to pass through to the intensifier tube. There is a ceiling
of around 5-7x which is the highest magnification you can collect enough light
to see objects at their ultimate distance. Weapons Mountable night vision continues
to grow in popularity, namely to the rise of wild hogs and to varmint hunting.
Since both coyotes and pigs are nocturnal and active at night, use of night
vision in the field has been a game changer in detecting, identifying and
harvesting these animals.
The key
difference between the night vision generations is the intensifier technology.
Gen1 was first developed in the Vietnam area, and is recognized as the now
entry level into night vision devices. Gen1 devices use an intensifier tube
that amplifies ambient light by accelerating electrons and striking a green
phosphor surface (just like a television).Gen1 used under optimal conditions
give you 75-100 yds visibility. Gen2 devices have added a micro-channel plate
that multiplies the number of electrons before they make contact on the
phosphor screen (thus increasing clarity, quality and brightness). Gen2 devices
can come in white or green phosphor variants. The white phosphor typically run
more, as they provide enhanced clarity, as well as lower eye fatigue. Gen2
devices under optical conditions can expect visibility in 150-200 yds. Gen3 is
currently what the US Military uses andhave added a Gallium Arsenide
photocathode which creates significantly more photoelectrons than Gen2 devices
andis more efficient at amplifying existing light or IR illumination. Gen3
devices are significantly brighter and better in optical clarity than other
generations and under optimal conditions allow visibility out to 350-400 yds. Lastly,
Digital Night Vision was released in the early 2000’s, as it plays on same
principal as your NV modes on digital cameras. Digital NV uses CCD (charged
coupling devices) to process light prior to sending to an LCD (liquid crystal
display) image. Utilizing this technology, Digital NV is not damaged by large
amount of natural light and are able to be used in both night and day. As with
most technology Digital NV has offered a significant bang for your buck, as it
is typically cost comparative to Gen1 devices, but offers resolution and clarity
of a Gen2 device.
Ultimately the best solution comes down to how
you will use the device and what are the features you desire most. Thermal is
best used for detection purposes, as you can quickly and easily notice objects
that are otherwise hidden from view. Night vision since used as an optical
system is a significantly clearer image and allows you to see all areas in
night such as holes in the ground, brush, etc. and is truly like turning on the
lights. Both of these technologies are a true asset to have with you while
hunting at night.
You can find more information about night vision here:
How do night vision cameras work?
How Does Night Vision Work?
In our store
Table of contents
Featured Articles
Most people have seen night vision technology in movies but don't know how it work’s. In this article, we are going to tell you who, where and why nig..
Night vision vs. thermal optics: what you need to know. A brief description of both technologies and their positive and negative qualities. The main d..
Night Vision Devices are a serious investment. Following these simple rules can protect it (and you) from harm while allowing you to enjoy all of the ..
Focusing on variances in technology within security cameras, this addresses how security cameras work utilizing night vision technology..
Night Vision technology has developed significantly since first introduced 75 yrs ago, the article below highlights some of these breakthroughs as wel..